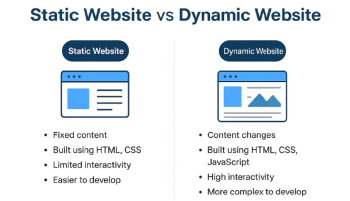
1. What is a Dynamic Website?
A dynamic website changes its content automatically based on user interactions or data stored in a database.
For example:
-
A news site updates stories without you editing HTML files every time.
-
An e-commerce store loads products from a database.
-
A social media page displays posts from multiple users.
Unlike static websites (HTML + CSS only), dynamic websites can:
-
Show different content for different users.
-
Store and retrieve data from a database.
-
Be interactive with real-time updates.
2. What You Need
To create a dynamic website, you’ll need:
-
HTML – For structure of the web page.
-
CSS – For styling and design.
-
JavaScript – For interactivity on the browser side.
-
A server-side language – PHP, Node.js, Python, etc.
-
A database – MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, etc.
-
A web server – Apache, Nginx, or a hosting service.
3. How It Works (Simple Flow)
User visits website → Request goes to the server
Server fetches data from the database → Generates HTML dynamically
Browser displays the updated page to the user
4. Step-by-Step Example
Here’s a basic dynamic site using PHP + MySQL:
Step 1: Setup Your Environment
-
Install XAMPP or WAMP (includes Apache, PHP, MySQL).
-
Create a folder inside
htdocs(e.g.,mywebsite).
Step 2: Create the Database
CREATE DATABASE mywebsite;
USE mywebsite;
CREATE TABLE posts (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(255),
content TEXT
);
INSERT INTO posts (title, content) VALUES
('First Post', 'This is my first dynamic post.'),
('Second Post', 'This content comes from the database!');
Step 3: Create index.php
<?php
$connection = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "mywebsite");
$result = $connection->query("SELECT * FROM posts");
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Dynamic Website</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial; max-width: 700px; margin: auto; }
.post { border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; margin-bottom: 20px; }
h2 { color: #333; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Dynamic Website</h1>
<?php while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()): ?>
<div class="post">
<h2><?= $row['title'] ?></h2>
<p><?= $row['content'] ?></p>
</div>
<?php endwhile; ?>
</body>
</html>
Step 4: Run the Website
-
Start Apache and MySQL in XAMPP.
-
Visit
http://localhost/mywebsite/in your browser. -
You’ll see posts loaded dynamically from your database.
5. Next Steps
Once you master the basics, you can:
-
Add forms to insert data into the database.
-
Use AJAX for real-time updates.
-
Apply frameworks like Laravel (PHP) or Express (Node.js) for scalability.
-
Deploy your website online using hosting providers.
✅ Key Takeaway:
A dynamic website connects frontend (HTML, CSS, JS) with a backend (PHP, Node, etc.) and a database to deliver personalized and changing content automatically.