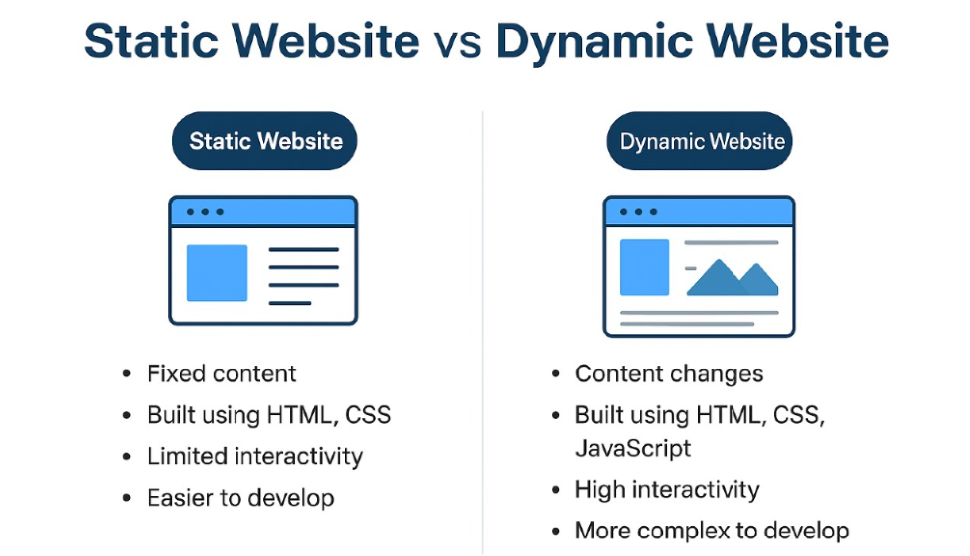
1. Difference Between Static Website and Dynamic Website
| Feature | Static Website | Dynamic Website |
|---|---|---|
| Content | Fixed — the same for every visitor until manually changed by a developer. | Changes automatically based on user interaction, database content, or other inputs. |
| Technology | HTML, CSS, sometimes basic JavaScript. | HTML, CSS, JavaScript + server-side languages (PHP, Python, Node.js, ASP.NET, etc.) and databases (MySQL, MongoDB, etc.). |
| Interactivity | Very limited (only basic forms or client-side scripts). | Highly interactive (login systems, search functions, e-commerce carts, dashboards, etc.). |
| Data Source | Stored directly in HTML files. | Data is fetched from databases or APIs in real-time. |
| Development Time | Faster to create, lower cost. | Takes longer to build, higher cost. |
| Maintenance | Must manually edit each file to update content. | Easy to update via CMS (like WordPress, Drupal) or admin panels. |
| Example | Personal portfolio with fixed text/images. | Facebook, Amazon, Gmail, Netflix. |
2. Detailed Information About Dynamic Websites
A dynamic website is one whose content changes based on user actions, database queries, or server-side processing. It’s built to respond in real time, making it flexible, interactive, and personalized.
Key Features
-
Database Integration
-
Stores content, user data, and configurations in a database.
-
Example: When you log into your Gmail, it fetches your emails from a database.
-
-
Personalization
-
Content changes based on the user — e.g., Amazon shows different product recommendations for each visitor.
-
-
Real-time Updates
-
Displays live data (e.g., sports scores, stock prices, chat messages) without needing a full page reload.
-
-
User Interaction
-
Forms, comment sections, search bars, shopping carts — all processed dynamically.
-
-
Content Management System (CMS)
-
Non-technical users can update content via an admin dashboard without coding.
-
Examples: WordPress, Joomla, Drupal.
-
Technologies Used
-
Frontend (Client-side):
-
HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular.
-
-
Backend (Server-side):
-
Languages: PHP, Python (Django, Flask), Java (Spring), JavaScript (Node.js), Ruby (Rails).
-
Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB.
-
-
APIs & AJAX
-
For asynchronous data updates without page reload.
-
Types of Dynamic Websites
-
Server-Side Dynamic Websites
-
Content is generated on the server before sending to the browser.
-
Example: PHP scripts rendering HTML from a MySQL database.
-
-
Client-Side Dynamic Websites
-
Content changes in the browser using JavaScript without reloading the page.
-
Example: Single Page Applications (SPAs) like Gmail.
-
Advantages
-
Easy content updates.
-
Personalized user experiences.
-
High interactivity.
-
Can handle large-scale applications.
Disadvantages
-
More complex to build and maintain.
-
Requires hosting with server-side processing capabilities.
-
Higher development and maintenance cost.
If you want, I can also make you a visual diagram comparing static and dynamic websites so it’s easier to remember.
Do you want me to make that diagram for you?